A Patient’s Guide to Olecranon Bursitis—Swelling at the Back of the Elbow
Elbow bursitis occurs in the olecranon bursa, a thin, fluid-filled sac that is located at the boney tip of the elbow (the olecranon).
There are many bursae located throughout the body that act as cushions between bones and soft tissues, such as skin. They contain a small amount of lubricating fluid that allows the soft tissues to move freely over the underlying bone.
Normally, the olecranon bursa is flat. If it becomes irritated or inflamed, more fluid will accumulate in the bursa and bursitis will develop.
Anatomy
The elbow serves two distinct functions: 1) to bend and straighten 2) to turn the palm up and palm down. The elbow utilizes three bones in articulation to accomplish these purposes—humerus, ulna, and radius.
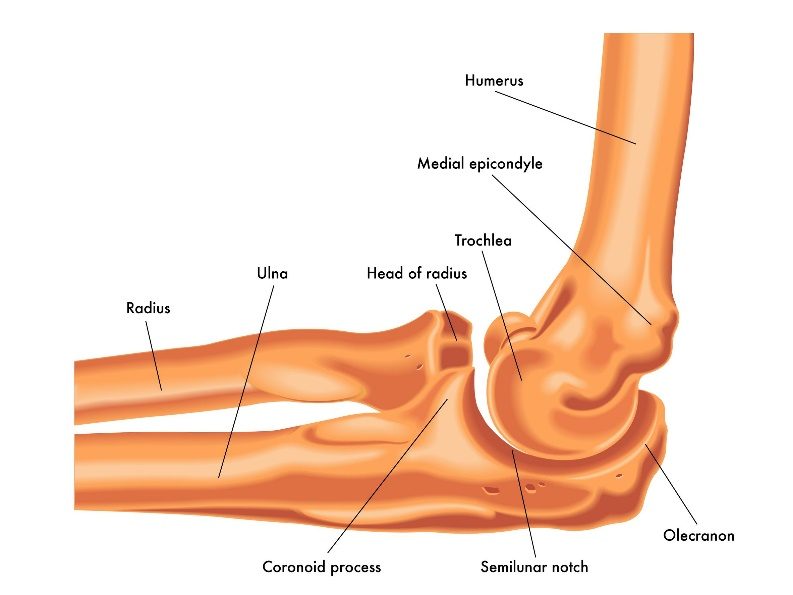
Lateral view of a right elbow demonstrating humerus, ulna, and radius (arrow pointing toward olecranon process of the ulna).
The olecranon is the tip of the ulna and serves as the insertion point for the triceps muscle—which straightens the elbow.
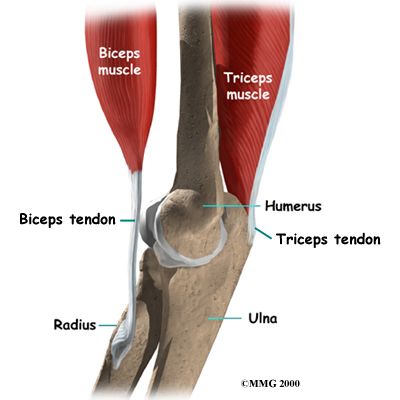
The triceps muscle inserts into the olecranon process of the elbow and straightens the elbow. The biceps inserts into the radius and bends the elbow.
The bones of the elbow are held together by joint capsule, ligaments and tendons. As we age, the strength of both ligaments and bones decrease over time.
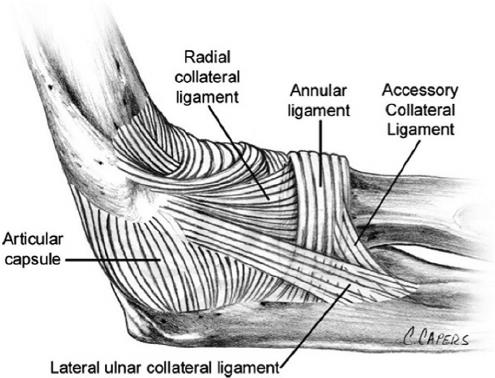
Ligaments of the elbow viewed from the lateral aspect
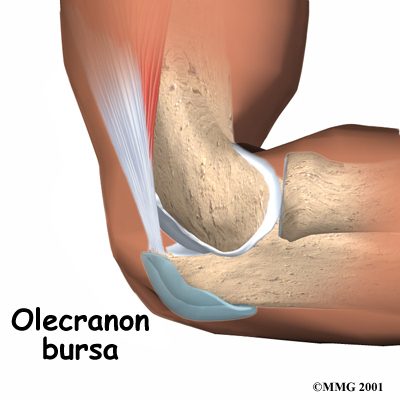
The Olecranon bursae serves as a buffer between the bony olecranon process and the overlying skin
Diagnosis
Symptoms
Patients who experience olecranon bursitis present with pain, swelling and often bruising over time. There may be deformity of the arm dependent upon the degree of displacement of the fracture. If the bursae is infected, it may exhibit warmth and redness.
Physician Exam
After taking a history and noting your symptoms, a physical exam is then performed by the surgeon. The status of the vascular supply to the hand is observed. Similarly the sensation and motion of digits are noted
Imaging
X-rays are indicated to determine the bones which have been injured and if there are any dislocations associated with the injury. X-rays may be taken from several angles to better delineate the fracture.
An aspiration of the fluid may be obtained. This is typically done if there is a question of infection, although the vast majority of olecranon bursitis is traumatic—not septic. The fluid may be sent for analysis and also for culture.
Treatment
Nonoperative
If your doctor suspects that bursitis is due to an infection, he or she may recommend aspirating (removing the fluid from) the bursa with a needle. This is commonly performed as an office procedure. Fluid removal helps relieve symptoms and gives your doctor a sample that can be looked at in a laboratory to identify if any bacteria are present. This also lets your doctor know if a specific antibiotic is needed to fight the infection
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics before the exact type of infection is identified. This is done to prevent the infection from progressing. The antibiotic that your doctor prescribes at this point will treat a number of possible infections.
If the bursitis is not from an infection, there are several management options.
- Elbow pads.An elbow pad may be used to cushion your elbow.
- Activity changes.Avoid activities that cause direct pressure to your swollen elbow
Over 90% of olecranon bursitis patients will respond to padding/activity modifications over 2 months of treatment
Operative
Surgery for an infected bursa. If the bursa is infected and it does not improve with antibiotics or by removing fluid from the elbow, surgery to remove the entire bursa may be needed. This surgery may be combined with further use of oral or intravenous antibiotics. The bursa usually grows back as a non-inflamed, normally functioning bursa over a period of several months.
Surgery for the noninfected bursa. If elbow bursitis is not a result of infection, surgery may still be recommended if nonsurgical treatments do not work. In this case, surgery to remove the bursa is usually performed as an outpatient procedure. The surgery does not disturb any muscle, ligament, or joint structures.
Rehabilitation
After surgery the arm is immobilized in a splint to allow for wound healing. Patients report pain after surgery, but the pain generally improves. Initiation of range of motion causes soreness for many patients. Typically, formal physical therapy is not required.
Recovery times vary greatly depending upon the presence of infection and need for intravenous antibiotics. If would healing is successful, padding and protection of the wound may be continued for several months after surgery. Recurrence of the bursitis may occur as well as stiffness. Other complications can include continued infection, nerve injury, and wound issues.


